History of Artificial Intelligence
Alan Turing

Alan Turing (1912-1954) is known as the "father of AI" because he laid the foundation for computer science with concepts such as the Turing Machine and the Turing Test. The Turing Machine helps us understand how a machine can behave like a human. At the same time, the Turing Test assesses a machine's ability to perform computations—such as reading and writing—faster than a human and to solve problems effectively.
Historical Life
The first creation of AI started with Alan Mathison Turing. Turing was the first British computer developer in the year-the mid-20th century.
In 1935, Turing explained the concept/ theory of the computing machine that it has unlimited memory and installed a scanner that moves in different directions and sends it to the memory. The scanner reads the program instructions kept in storage memory as symbols and then does the action.
World War 2 was a battle between England and Germany. Alan Turing participated in this war, hoping for a bright future through his understanding of cryptanalysts and destroying the German Enigma code. German updated a basic typewriting machine into a large one called the German cyphering machine Enigma. This machine has a generator that randomizes billions of combinations. As complex as it was, this wasn't a challenge for Alan Turing. He and different mathematicians from Bletchley Park managed to hack the Enigma code quickly after joining the organization. He and his team created a machine, bombe, that“mimicked the workings of Enigma's rotors to test potential ciphers”(Castro 2025)
In Bletchley Park, Turing emphasizes the idea of Machine intelligence by referring to chess. This is an excellent way for computers to solve a problem and provide a solution that can be tested. He thought that a chess-playing computer could think through multiple moves by examining other players playing the game, but he knew it was not possible because it would have to analyze "large number of moves."(Coopland 2025).In the year 1945, Turing dreamed that a computer was able to beat a person in chess, and in 1997, that what actually happen. In the 1997, there was a Deep Blue, a chess computer created by "IBM (International Business Machines Corporation)" that won against the world champion, "Garry Kasparov, in a six-game match."(Coopland 2025) Even though Turing's belief seems right, his belief that computers could understand how people think didn't come true. Computer engineering helped upgrade chess, but no further development in artificial intelligence was made.
In 1950, Turing was a producer that tested computer intelligence, which is called the Turing Test. The Turing test comprises the computer, the human interrogator, and a human foil. The interrogator's job is to identify who is a computer by asking a series of questions to both participants(one of them is the computer). Communication works by typing information on the keyboard and outputting the information off the computer screen. The interrogators can ask various questions, and the computer has to respond in a way that isn't the wrong identification. For instance, a computer might say "No" to "Are you a computer" and pretend to be a human being. If the interrogator is wrong, mistaking a computer for a human being, then the computer has the same intelligence as a human being.
History of Artificial Intelligence
John McCarthy

John McCarthy (1927-2011) developed the phrase "Artificial intelligence" and created the programming language called LISP, which is a program that can change symbols with a series of algorithms. This created the fundamentals of computer science(CS). He also made different types of time-sharing systems. The internet wouldn't have been here if it wasn't for him developing the time-sharing system. Time-sharing is what we used to know as servers and cloud computers. LISP was a helpful tool in the program. In AI, he made the theory of time-sharing and AI problem-solving.
Historical
McCarthy was born in 1927 in Boston, Massachusetts. He loved mathematics and logic. When he was fifteen, he purchased a textbook from the California Institute of Technology (Caltech) and became self-educated in calculus. After enrolling in Caltech, he took many calculus courses and graduate courses. He did worse in physical education since he avoided attending classes, eventually getting him drafted into the Army. He later came to Caltech and earned a bachelor's in science and mathematics in 1948. The following year, he went to a different university, Princeton, and majored in mathematics. At this university, he and his friend, Marvin Minsky, then graduated. Between 1951 and 1953, McCarthy was a professor who taught mathematics at Princeton.
In 1955, McCarthy became a professor's helper at Dartmouth College. During his time there, he created a conference where the most intelligent people in the computer field came together. At this very moment, McCarthy coined the term AI (artificial intelligence). This gave birth to the 1956 Dartmouth Conference, the beginning of Artificial intelligence. In 1957, McCarthy headed to the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) to the Computation Center to study throughout the one-year course. He didn't visit Dartmouth.
After living at MIT, McCarthy recommended allowing more than one person to interact with computers instead of one computer, which is well-known as time sharing. Computers were expensive, and few people could afford them during this time. An example of a computer used during this time was the “batching processing systems.” (Christopher 2023).According to John McCarthy, “The batch” referred to a set of punch cards, and the implication was that only one user could work with a computer at a time. For each computer program to be run, programmers waited for the card reader to process the punch cards, the results to be calculated, and the output to be printed. It became clear that the processor was active for only a small part of that time, and given that the machines were costly, that idle time represented wasted money.” (Christopher 2023). This means that batch is an example of a computer that can be used once for a person at a time, which is very limited and time-consuming for a person who doesn't have time to chip in their card, but McCarthy thought of a plan to resolve this issue.
In 1955, McCarthy became a professor helper at Dartmouth College. At Dartmouth, he created a conference where the most intelligent people in the computer field came together. At this very moment, McCarthy coined the term AI (artificial intelligence). This gave birth to the 1956 Dartmouth Conference, the beginning of Artificial intelligence. In 1957, McCarthy headed to the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) to the Computation Center to study throughout the one-year course. He didn’t visit Dartmouth.
In 1858, while continuing to work at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, McCarthy created a programming language called LISP, which is a program that can change symbols with a series of algorithms. This plays a massive part in the development of AI programming languages and the fundamentals of computer science. It can also develop symbolic information, which helps break down advanced AI systems anyone can learn from and apply.
Even though LISP isn't always used in today's society, it laid the foundation for the creation of the AI programming language.
Extra Information
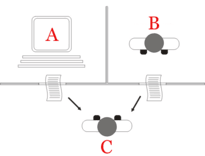
In the "Turing test," a person converses with a human and a robot in different rooms and must figure out which. If the robot is convincing, it passes the test.
Below is a frame where you can talk to and converse with the machine.
ClickButton to visit the Turing Test website.
LISP Explanation
Lists use simple notation in operation, and operands are appealed to them in a list. For instance, (+ a (* b c)) stands for a + b*c. The good thing about the list is that it can be used through different programming. In the article, LISP, LISP also uses the list structure to represent data, and because programs and data use the same structure, it is easy for a LISP program to operate on other programs as data.”(Hemmendinger 2025). This means that LISP is friendly programming that can be used across every language being that the fact the language programming is the same.
Here are a few examples of what a LISP programming looks like: